Choose the Right RCD for Your Needs
Introduction to The Ultimate Guide to RCDs
Residual Current Devices (RCDs) play a vital role in protecting electrical systems, ensuring safety from electric shocks, fire hazards, and damage to sensitive equipment. However, with various types of RCDs available—including time delay versions—it’s essential to understand their differences and applications. This guide explains everything you need to know about RCDs, how to select the right type, and the difference between RCDs and RCCBs.
Table of contents
1. What Are RCDs and Why Are They Important?
Residual Current Devices (RCDs) are safety devices designed to disconnect the power supply when they detect earth leakage currents. Unlike standard circuit breakers, which protect against overcurrent and short circuits, RCDs focus on preventing electric shocks and fire hazards caused by leakage currents.
Key benefits of RCDs include:
- Shock Protection: Especially for homes and outdoor circuits.
- Fire Prevention: Essential for industrial installations.
- Sensitive Equipment Protection: Ideal for safeguarding modern appliances.
2. Types of RCDs
30mA RCDs
30mA RCDs offer high sensitivity, making them suitable for protecting against electric shocks in residential and commercial setups.
- Applications: General circuits, garden lighting, and tools.
- Shop 30mA RCDs ➡️
100mA RCDs
These RCDs focus on fire prevention and are typically used in circuits where shock protection is less critical.
- Applications: Fire safety in commercial or agricultural settings.
- Shop 100mA RCDs ➡️
300mA RCDs
Designed for industrial and heavy-duty applications, 300mA RCDs are primarily used to prevent fire hazards.
- Applications: Factories, warehouses, and industrial machinery.
- Shop 300mA RCDs ➡️
Type A RCDs
Type A RCDs are designed for circuits with electronic components, capable of detecting pulsating DC currents and alternating currents.
- Applications: LED lighting, washing machines, and induction hobs.
- Shop Type A RCDs ➡️
Time Delay Type A RCDs
Time delay RCDs (also known as Type S) incorporate a delayed trip mechanism to allow discrimination with downstream devices. This ensures that only the circuit with the fault trips, preventing unnecessary power cuts.
- Applications: Fire protection in industrial setups, upstream in cascaded systems.
- Key Feature: Cannot be used for personal shock protection due to delayed operation.
- Shop Time Delay Type A RCDs ➡️
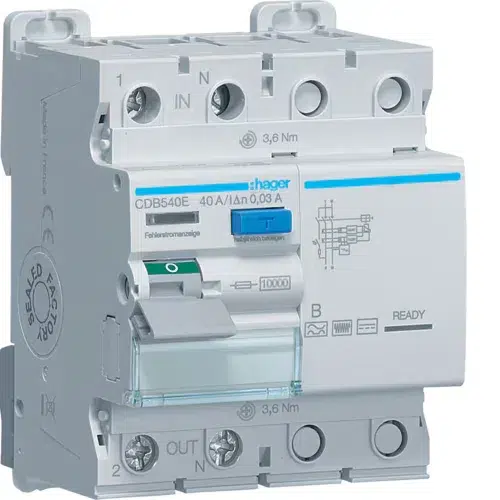
Type B RCDs
Type B RCDs are designed for advanced systems where DC leakage currents exceed 6mA. These are critical for renewable energy systems and EV charging stations.
- Applications: EV chargers, PV systems, and industrial equipment.
- Shop Type B RCDs ➡️
Type F RCDs
Type F RCDs are ideal for appliances with frequency-controlled motors or drives, such as modern air conditioning units or washing machines.
- Applications: Variable-speed drives, synchronous motors, and certain tools.
- Shop Type F RCDs ➡️
3. Difference Between RCD and RCCB
While the terms RCD and RCCB are often used interchangeably, they have specific meanings:
- RCD (Residual Current Device): A generic term for devices that detect residual current and disconnect the circuit. This includes RCCBs, RCBOs, and SRCDs.
- RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker): A specific type of RCD that provides residual current protection but does not offer overcurrent protection.
Key Differences:
| Feature | RCD | RCCB |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Generic term for residual current protection devices | Specific device without overload or short-circuit protection |
| Examples | RCCB, RCBO, SRCD, PRCD | Standalone residual current breaker |
| Overload Protection | May include overload protection (e.g., RCBO) | No overload protection |
4. How to Choose the Right RCD
To select the correct RCD, consider the following:
- Application Type: Residential, commercial, or industrial.
- Equipment in Use: Determine whether appliances generate DC leakage currents or use variable-speed drives.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure compatibility with BS 7671 and manufacturer guidelines.
- Discrimination: Use time delay RCDs upstream for cascaded systems.
5. Shop RCDs at Electrical4Less
Electrical4Less offers an extensive range of RCDs for all applications:
6. FAQs About RCDs
What is the difference between an RCD and an RCCB?
An RCCB is a type of RCD that specifically provides residual current protection without overload or short-circuit protection.
Why use a Time Delay Type A RCD?
Time delay RCDs allow selectivity in systems with multiple RCDs, ensuring only the affected circuit trips while upstream circuits remain powered.
Are Type AC RCDs still used?
Type AC RCDs are becoming less common due to their inability to handle DC leakage currents. Type A, F, or B are preferred for modern systems.
Do I need a Type B RCD for an EV charger?
Yes, most EV chargers require Type B RCDs due to the potential for high DC leakage currents.
How often should I test my RCD?
Press the test button every three months to ensure proper functionality.
7. Follow Electrical4Less on Social Media
Stay updated with the latest in electrical safety and products by following Electrical4Less on social media.
- YouTube: Watch detailed product demos, installation guides, and safety tips. Visit our YouTube channel ➡️
- Instagram: See real-world applications of our products and exciting new arrivals. Follow us on Instagram ➡️
- Facebook: Join the community for updates, deals, and expert advice. Connect with us on Facebook ➡️
Conclusion
RCDs are essential for protecting electrical systems, equipment, and lives. Understanding the different types—including time delay versions—helps you choose the right device for your installation. At Electrical4Less, we offer high-quality RCDs for every need. Explore our range today and ensure your safety and compliance.. Thank you for reading “The Ultimate Guide to RCDs”
- Compact Horizontal TP&N Distribution Boards – With 100A Main Switch & Type 2 SPD Options
- 🧱 Large PVC Cable Trunking by Dietzel Univolt – Key Sizes + Accessories
- How to Choose an LED Driver – Constant Voltage vs Constant Current Explained
- Most Popular FuseBox Consumer Units
- 🔌 Commando Sockets – The Ultimate Guide to Industrial Plugs and Sockets (IEC 60309)