Your Guide to Efficient TPN Boards
In any large-scale commercial or industrial electrical installation, efficiency and safety are critical. Enter the three phase distribution board—a cornerstone of modern electrical systems. These boards, commonly referred to as TPN boards, manage power distribution in a way that maximizes efficiency and ensures protection for your circuits and equipment.
This in-depth guide will walk you through everything you need to know about three phase distribution boards: what they are, how they work, why they matter, and the different brands and components that make up these essential systems. If you’re a contractor, electrician, or facility manager, understanding the intricacies of these boards can help you make informed decisions and ensure the longevity of your electrical installations.
Table of contents
- Your Guide to Efficient TPN Boards
- 1. What is a Three Phase Distribution Board?
- 2. Why Do You Need a Three Phase Distribution Board?
- 3. Key Components of Three Phase Distribution Boards
- 4. Three Phase vs Single Phase: What’s the Difference?
- 5. Choosing the Right Three Phase Distribution Board
- 6. Popular Brands: Fusebox, Hager, and Live
- 7. Three Phase Circuit Protection Devices: MCBs, RCDs, SPDs
- 8. Installation Best Practices for Three Phase Distribution Boards
- 9. Regulations and Compliance
- 10. Conclusion: The Role of Three Phase Distribution Boards in Modern Installations
1. What is a Three Phase Distribution Board?
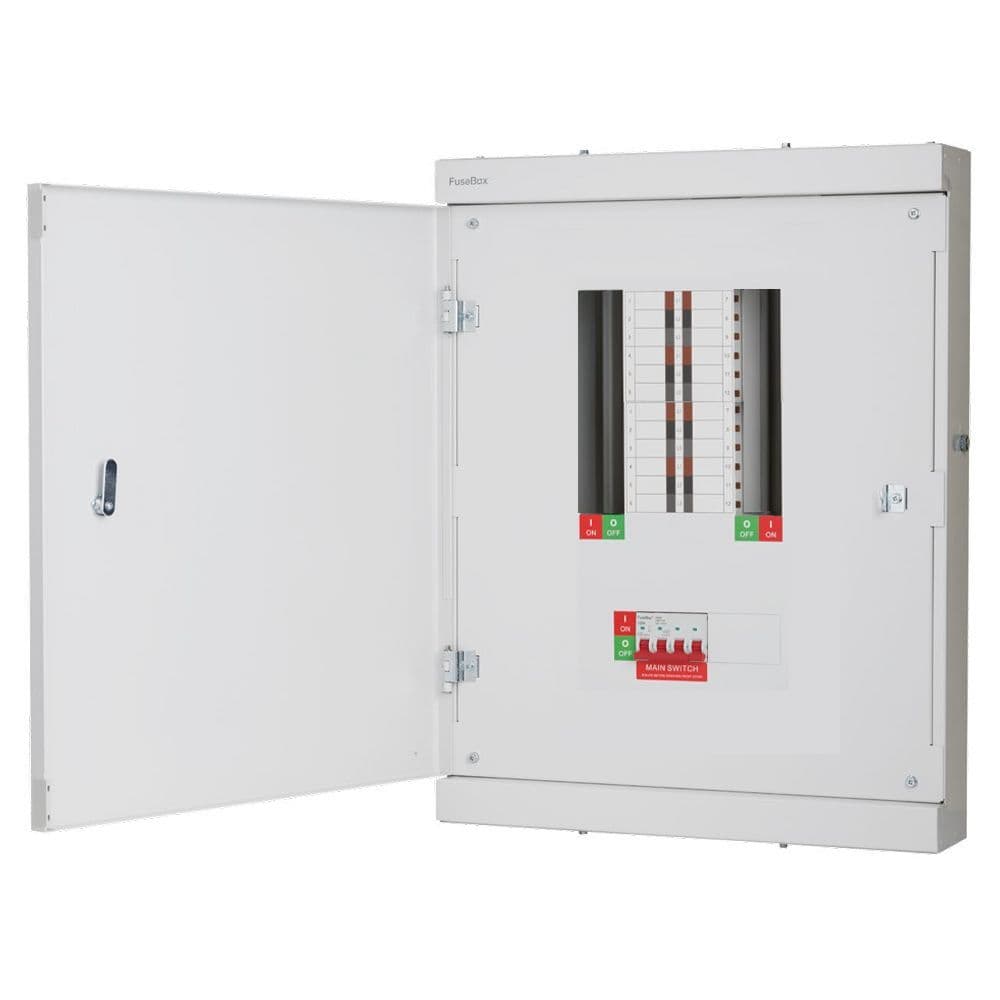
A three phase distribution board is a key electrical component designed to distribute power across multiple circuits in a three-phase system. Unlike single-phase systems, which deliver power through one live wire and a neutral, three-phase systems use three live wires, delivering more power and creating a more balanced electrical load.
These boards are used predominantly in commercial and industrial settings where large amounts of power are needed. The primary function of a three-phase board is to distribute electrical power efficiently while providing protection from overloads, short circuits, and other electrical faults.
TPN Boards: A Technical Overview
The term TPN stands for Three Phase and Neutral, which describes how these boards distribute power. Each phase carries 120 degrees of electrical power, and the neutral wire helps stabilize the current. TPN boards are essential in maintaining a balanced and efficient electrical flow, even under heavy loads.
Three Phase Consumer Units
In addition to TPN boards, you’ll often hear the term three phase consumer units, especially in smaller commercial setups. Consumer units are designed to handle smaller loads but serve the same function: distributing power safely and efficiently across multiple circuits.
2. Why Do You Need a Three Phase Distribution Board?
A three phase distribution board is vital in any electrical system that handles substantial energy demands. But why is it so crucial? Let’s break down its importance:
1. High Power Capacity
Unlike single-phase systems, which can struggle under heavy loads, three-phase systems are designed to handle higher electrical demands. A three-phase distribution board efficiently manages power for large machinery, HVAC systems, elevators, and other equipment typically found in industrial or commercial spaces.
2. Balanced Power Distribution
One of the key advantages of a three-phase system is that it balances the electrical load across three phases, reducing strain on any single circuit. This balance leads to smoother operation and reduces the risk of power surges or electrical faults.
3. Enhanced Safety
A well-configured three-phase distribution board not only optimizes power distribution but also enhances safety by incorporating protective devices like MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers), RCDs (Residual Current Devices), and SPDs (Surge Protection Devices), all of which safeguard your electrical system from faults.
4. Energy Efficiency
Three-phase systems are inherently more efficient than single-phase systems, especially in environments that use high-powered equipment. With less energy lost during transmission, three-phase distribution boards help reduce energy costs in the long term.
3. Key Components of Three Phase Distribution Boards
To fully understand how a three phase distribution board works, it’s important to know its main components. Each plays a critical role in ensuring that power is distributed safely and efficiently across all circuits.
1. Circuit Breakers (MCBs)
Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) are essential for protecting individual circuits from overcurrents. In a three-phase system, each phase will typically have its own MCB, which trips if the current exceeds a set limit.
2. Residual Current Devices (RCDs)
An RCD provides additional protection by detecting earth faults—when electrical current leaks from the circuit into the ground. This device immediately disconnects the circuit to prevent electrical shock and minimize fire risk.
3. Surge Protection Devices (SPDs)
Electrical surges can damage equipment and compromise the safety of your electrical installation. SPDs protect against voltage spikes by diverting excess voltage to the ground, safeguarding your equipment and circuits.
4. Busbars
The busbar is the metal strip that carries the electrical current within the distribution board. It connects the incoming power to each individual circuit, distributing the electrical load evenly.
5. Neutral and Earth Bars
In a TPN board, the neutral bar connects all neutral wires from the individual circuits, while the earth bar provides a common grounding point, ensuring safety in case of faults.
6. Main Switch
The main switch controls the entire distribution board. In case of an emergency or system maintenance, turning off the main switch will disconnect power to all circuits connected to the board.
4. Three Phase vs Single Phase: What’s the Difference?
It’s easy to get confused between single-phase and three-phase systems, but understanding their differences is crucial when choosing the right setup for your needs.
1. Power Distribution
- Single-phase systems deliver power using one live wire and one neutral wire. These systems are more common in homes and small businesses where the power demand is lower.
- Three-phase systems, on the other hand, use three live wires, distributing power in a more balanced way. This setup is ideal for industrial applications or large commercial properties with high energy requirements.
2. Efficiency
A three-phase system is much more efficient for heavy loads because it evenly distributes power across three wires. In contrast, a single-phase system can become overloaded more easily.
3. Applications
- Single-phase systems are often used for smaller applications such as lighting and household appliances.
- Three-phase systems are required for running heavy-duty equipment like industrial machines, elevators, and large heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems.
5. Choosing the Right Three Phase Distribution Board
Selecting the right three phase distribution board can be a daunting task, especially with so many options available. However, a few key considerations can help you make the best choice for your application.
1. Load Requirements
Understanding your total load requirements is crucial when selecting a three-phase board. Too small, and your board won’t be able to handle the demand. Too large, and you could be wasting energy. Always factor in both the immediate and future power needs of your installation.
2. Type of Circuit Protection
Different applications require different levels of protection. For example, if you’re installing a board in an area prone to electrical surges, you may need enhanced SPD protection. If the board will be serving sensitive equipment, RCDs should also be a priority.
3. Space Considerations
Not all installations have the luxury of ample space. Make sure that the board you select fits comfortably in the allocated area, with enough room for safe maintenance.
4. Quality and Compliance
Always choose high-quality boards from trusted manufacturers that comply with industry standards and safety regulations. Leading brands like Fusebox, Hager, and Live are known for their compliance with UK regulations and long-lasting performance.
6. Popular Brands: Fusebox, Hager, and Live
Let’s dive deeper into the top brands that manufacture three phase distribution boards. These companies are industry leaders, known for their innovation, reliability, and adherence to safety standards.
1. Fusebox Three Phase Boards
Fusebox has a solid reputation for offering robust, high-performance TPN boards and three phase consumer units. Their boards come equipped with top-notch safety features like MCBs, RCDs, and SPDs. Fusebox TPN boards are ideal for both commercial and industrial applications, designed with ease of installation and maintenance in mind.
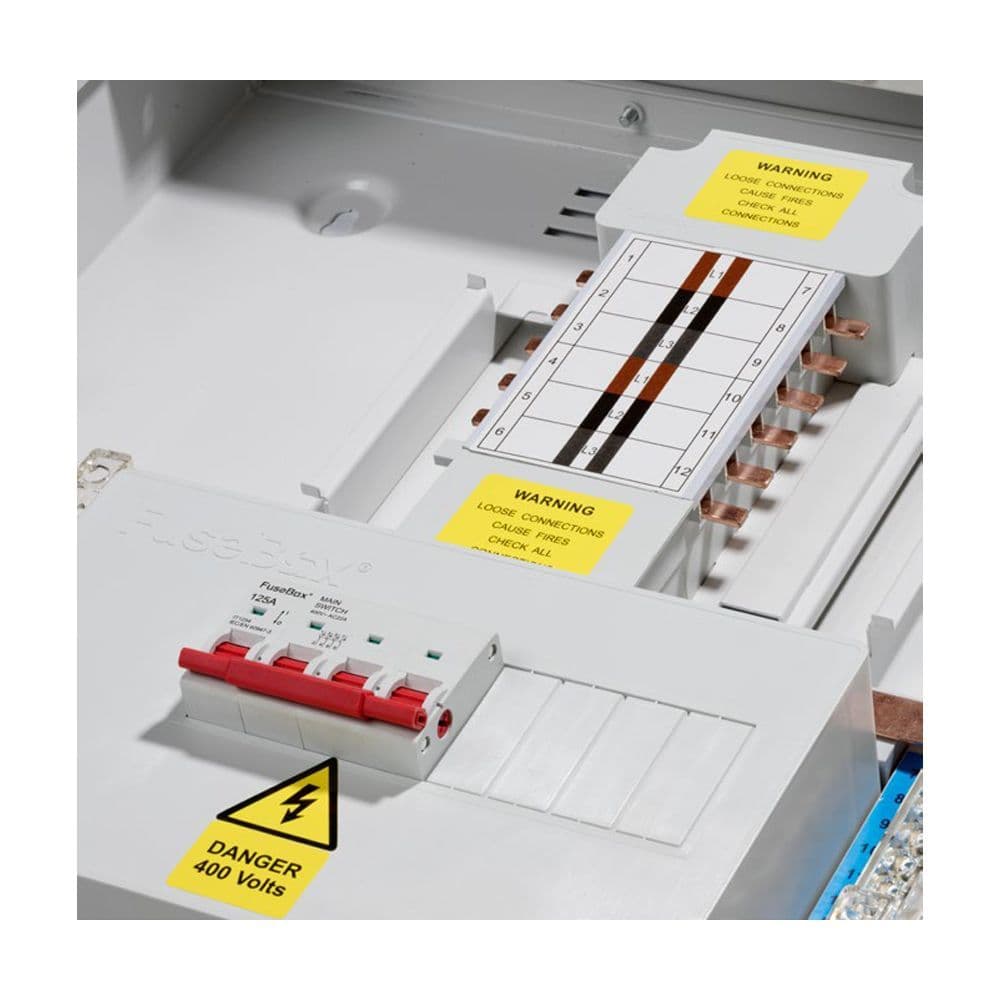

2. Hager Three Phase Boards
Another major player is Hager, a brand known for innovation in the electrical space. Hager TPN boards are designed for heavy-duty use and offer exceptional reliability. With a focus on safety and durability, Hager three phase boards feature premium components, from robust busbars to high-quality circuit breakers.
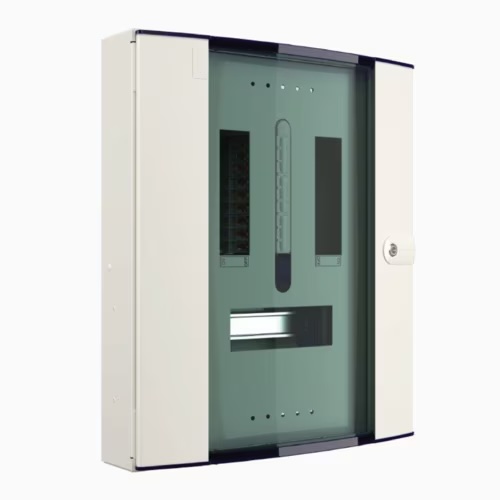

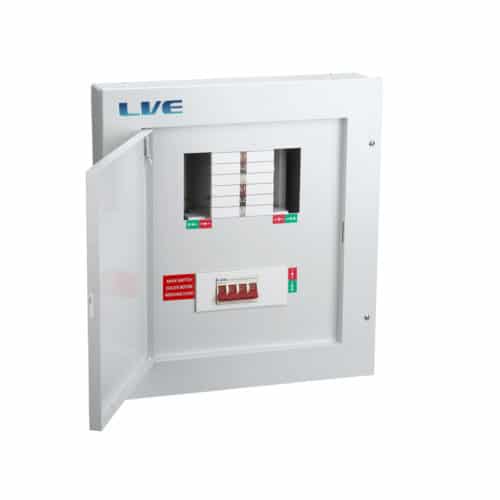
3. Live
Live offers flexible solutions for various electrical setups, and their three phase distribution boards are no exception. Their boards are known for affordability without compromising on safety and quality, making them a preferred choice for cost-conscious projects. Live also produces various accessories that integrate seamlessly with their boards, providing a complete solution for modern electrical installations.

7. Three Phase Circuit Protection Devices: MCBs, RCDs, SPDs
No three-phase distribution system is complete without the right circuit protection devices. These devices are critical to preventing electrical faults and ensuring the longevity of your system.
1. MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers)
An MCB protects your circuits from overcurrent, which occurs when there’s more electricity flowing through the circuit than it can handle. When an MCB detects an overload or short circuit, it trips, cutting off the power to prevent damage.
2. RCDs (Residual Current Devices)
An RCD adds an extra layer of protection by monitoring the current flow. If it detects that some of the current is leaking to the ground (indicative of a fault), it shuts down the circuit immediately, protecting against electric shock and reducing fire risk.
3. SPDs (Surge Protection Devices)
SPDs guard your electrical system against sudden surges in voltage, which can occur due to lightning strikes or power grid fluctuations. These surges can severely damage sensitive equipment, but with an SPD in place, excess voltage is safely diverted.
8. Installation Best Practices for Three Phase Distribution Boards
Installing a three phase distribution board requires precision, expertise, and a thorough understanding of the regulations. Here are some best practices to follow during installation:
1. Hire a Qualified Electrician
First and foremost, always work with a certified electrician. Installing a three-phase system is complex and can be dangerous if not handled correctly.
2. Plan Your Circuit Layout
Ensure that your circuit layout is carefully planned to avoid overloading any single phase. Distribute your circuits evenly across the three phases to maintain balance.
3. Use Proper Enclosures
Three-phase boards should be housed in weather-resistant enclosures if they’re installed in environments where moisture, dust, or extreme temperatures are present.
4. Grounding is Critical
Ensure that the neutral and earth bars are correctly wired to provide an effective grounding system. This is essential for protecting against electric shock and ensuring system safety.
9. Regulations and Compliance
Compliance with UK electrical regulations is non-negotiable when installing three phase distribution boards. The relevant standards are outlined in the IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671), which specify how electrical installations should be designed, installed, and tested.
1. Key Regulations to Follow
- Ensure that all installations are compliant with Part P of the Building Regulations, which relates to electrical safety in dwellings.
- All components, including MCBs, RCDs, and SPDs, should meet the IEC 60947 standards for low-voltage switchgear.
2. Inspection and Testing
After installation, your three phase distribution board should be inspected and tested by a qualified electrician to ensure compliance with the latest safety standards.
10. Conclusion: The Role of Three Phase Distribution Boards in Modern Installations
In any large-scale electrical installation, whether it’s a commercial office, factory, or industrial plant, three phase distribution boards play a vital role. These boards provide an efficient way to distribute power, protect equipment, and ensure safety across all circuits.
From understanding the different components like MCBs, RCDs, and SPDs to selecting trusted brands like Fusebox, Hager, and Live, there’s a lot to consider when designing or upgrading your electrical systems.
If you’re looking for efficient, safe, and reliable power distribution, three-phase systems are an excellent choice, and with the right distribution board in place, you can meet even the most demanding electrical needs.
See our full three phase distribution boards here!
Three Phase Distribution Boards FAQ
A three phase distribution board distributes electrical power across multiple circuits in a three-phase electrical system, commonly used in industrial and commercial settings.
It distributes electricity from the incoming power source to various circuits, balancing the load across three phases and protecting against faults with devices like MCBs, RCDs, and SPDs.
TPN boards refer to Three Phase and Neutral distribution boards, which distribute power across three live wires and one neutral wire.
While possible, three phase distribution boards are typically used in commercial and industrial installations where higher power demands exist.
A three phase consumer unit is used in smaller installations like commercial offices, while a three phase distribution board is for larger setups.