The Ultimate Guide to Protecting Your Consumer Unit With Type A RCBOs
In an age where electrical safety is more important than ever, understanding the devices that protect your home’s wiring system is crucial. Type A RCBOs are one of those essential components, combining the benefits of overcurrent protection with earth fault detection. Whether you’re a homeowner, electrician, or business owner, investing in the right RCBO can make all the difference when it comes to safeguarding both people and property.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into Type A RCBOs—what they are, why they matter, and how they compare to other types of circuit breakers. We’ll also cover the differences between single pole and double pole RCBOs, the growing significance of bidirectional RCBOs, and how to choose the best option for your specific electrical needs.
Table of contents
- The Ultimate Guide to Protecting Your Consumer Unit With Type A RCBOs
- 1. What is a Type A RCBO?
- 2. Why is a Type A RCBO Important?
- 3. How Does a Type A RCBO Work?
- 4. Single Pole vs Double Pole RCBOs: Which Should You Use?
- 5. Understanding Bidirectional RCBOs in Modern Installations
- 6. The Key Benefits of Using a Type A RCBO
- 7. Installation and Best Practices for Type A RCBOs
- 8. Type A RCBO vs. Type AC RCBO: What’s the Difference?
- 9. How Type A RCBOs Fit Into Regulatory Standards
- 10. Choosing the Right RCBO for Your Electrical System
- 11. The Future of Type A RCBOs and Renewable Energy
- 12. Common Issues and Troubleshooting RCBOs
- 13. Conclusion
1. What is a Type A RCBO?
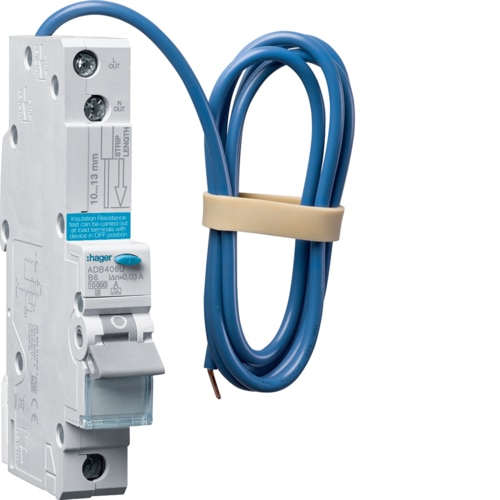
At its core, a Type A RCBO (Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent Protection) is a multifunctional electrical device that protects your home’s electrical circuits in two critical ways:
- Overcurrent protection: Safeguards against overloads and short circuits.
- Earth fault protection: Detects imbalances in the electrical flow (e.g., when current leaks through a faulty wire, potentially causing electric shock).
The key difference with a Type A RCBO compared to other types, like Type AC, is that it can detect both AC currents and pulsating DC currents. This makes it particularly well-suited for modern homes and workplaces that often use appliances with electronic components, such as computers, solar panels, and electric vehicle chargers.

2. Why is a Type A RCBO Important?
In an era where we are increasingly reliant on electronic devices, the Type A RCBO has become an essential safety tool. Unlike older models (such as Type AC RCBOs), Type A RCBOs offer protection from pulsating DC currents as well as traditional AC currents. This makes them highly versatile and better suited for today’s electrical loads.
Imagine your home is a fortress, with its electrical wiring forming the walls. Every day, power flows through this wiring, feeding various appliances and devices. However, even the strongest fortress has its vulnerabilities. An overloaded circuit, faulty appliance, or unexpected earth fault can tear down the defenses, leading to fires or electric shocks. The Type A RCBO stands guard, ensuring that your home’s defenses remain intact.
3. How Does a Type A RCBO Work?
To truly understand the value of a Type A RCBO, it’s important to know how it works. At its simplest, an RCBO is always monitoring the current flow through a circuit. If it detects any imbalance—say, current flowing somewhere it shouldn’t, like through a person’s body—it cuts off power instantly.
Here’s how it does this:
- Overcurrent Protection: Like an MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker), the RCBO will trip when a circuit draws more current than it can safely handle. This protects the wiring from overheating and possibly causing a fire.
- Residual Current Protection: The RCBO also monitors the balance between the live and neutral conductors. If even a tiny amount of current is flowing somewhere else—like through an earth fault—the device trips.
But here’s what sets a Type A RCBO apart: it doesn’t just monitor traditional AC current. It can also detect pulsating DC currents, which are more common in modern appliances like LED lights, variable speed drives, and photovoltaic systems.
This ability makes Type A RCBOs the best choice for homes with a mix of traditional and modern electrical loads.
4. Single Pole vs Double Pole RCBOs: Which Should You Use?
When selecting an RCBO, one of the key decisions you’ll need to make is whether to choose a single pole or double pole RCBO. The difference between these two lies in how many conductors they disconnect when a fault is detected.
Single Pole RCBO
- Single pole RCBOs monitor and protect the live wire (phase) only.
- When a fault occurs, they disconnect the live conductor, but the neutral remains connected.
- These are often used in residential installations where neutral-to-earth faults are less likely.
Double Pole RCBO
- Double pole RCBOs, on the other hand, monitor both the live and neutral wires.
- In the event of a fault, they disconnect both conductors, offering enhanced protection.
- They are more common in commercial or industrial settings and where greater safety is required, such as in environments with sensitive electronic equipment or outdoor installations.
While a single pole RCBO is often sufficient for most homes, double pole RCBOs are an excellent option if you’re seeking added protection, particularly in areas prone to earth faults.
5. Understanding Bidirectional RCBOs in Modern Installations
With the increasing adoption of renewable energy systems like solar panels, we are seeing a shift in how electricity flows through a home. In the past, current only flowed from the grid into the home. Today, homes with solar panels or battery storage systems often export power back into the grid.
This is where bidirectional RCBOs come in. These devices are designed to handle electrical flow in both directions—importing power from the grid and exporting excess power. A bidirectional RCBO protects your home whether the power is flowing in or out, making it an essential device for anyone with a renewable energy system.
Imagine a typical day in a solar-powered home. During the day, your solar panels produce more energy than you need, sending excess electricity back to the grid. At night, when the sun goes down, you pull energy from the grid. A traditional RCBO might struggle to handle this two-way flow of power, but a bidirectional RCBO ensures that your home remains safe no matter which way the electricity is flowing.
6. The Key Benefits of Using a Type A RCBO
Let’s take a closer look at why Type A RCBOs are gaining popularity across both residential and commercial installations.
1. Comprehensive Protection
The biggest benefit of a Type A RCBO is that it protects against both overcurrent and earth faults, while also detecting pulsating DC currents. This makes it suitable for modern installations that include appliances such as LED lighting, computers, and power supplies.
2. Reduced Nuisance Tripping
Ever had a device trip your entire electrical system, even though it’s perfectly safe? Type A RCBOs are more sensitive to the kinds of currents used in modern appliances, reducing the risk of nuisance tripping that can occur with older devices.
3. Energy Efficiency
By automatically shutting off power when a fault is detected, Type A RCBOs prevent unnecessary electricity consumption and help keep your energy bills in check.
4. Adaptability to Renewable Energy
As mentioned earlier, Type A RCBOs, especially in their bidirectional form, are ideal for homes equipped with solar panels or other renewable energy sources. They keep your system safe regardless of the flow of electricity.
5. Enhanced Safety Standards
When compared to older devices like Type AC RCBOs, Type A RCBOs meet or exceed modern safety standards. This is critical, as electrical regulations become more stringent, ensuring your home or business complies with current safety codes.
7. Installation and Best Practices for Type A RCBOs
Installing a Type A RCBO should always be done by a qualified electrician. However, there are a few key points to consider when installing these devices:
1. Compatibility with Your Consumer Unit
Make sure your Type A RCBO is compatible with your existing consumer unit. This includes checking the physical dimensions as well as the rated current and trip sensitivity.
2. Proper Labeling
Each RCBO should be clearly labeled to identify which circuit it protects. This helps during troubleshooting or if an RCBO needs to be reset.
3. Regular Testing
All RCBOs come with a test button that should be used regularly (usually once every six months) to ensure the device is working correctly.
4. Proper Sizing
Ensure that your RCBOs are correctly rated for the circuits they are protecting. Overloading an RCBO can lead to premature failure or nuisance tripping.
8. Type A RCBO vs. Type AC RCBO: What’s the Difference?
You may be wondering: what’s the difference between a Type A RCBO and a Type AC RCBO? The answer lies in the types of currents they can detect.
- Type AC RCBOs can only detect traditional alternating current (AC), which was the standard for decades.
- Type A RCBOs can detect both AC and pulsating DC currents, which makes them more suitable for modern electrical installations.
For most modern homes, where you’re likely to have appliances like washing machines, computers, or solar panels, a Type A RCBO offers better protection.
9. How Type A RCBOs Fit Into Regulatory Standards
Electrical safety regulations are continually evolving to keep pace with technological advancements. In many countries, including the UK and EU, Type A RCBOs are now recommended or required for certain installations, particularly in homes with renewable energy systems or modern electronic appliances.
By installing a Type A RCBO, you not only protect your home from potential electrical hazards but also ensure compliance with current and future safety standards.
10. Choosing the Right RCBO for Your Electrical System
When choosing the right RCBO for your electrical system, there are several factors to consider:
- Current Rating: Ensure the RCBO is rated to handle the current expected on the circuit it’s protecting.
- Trip Sensitivity: Most residential RCBOs have a trip sensitivity of 30mA, which is sufficient to protect against electric shock and fire hazards.
- Pole Configuration: Decide whether you need a single pole or double pole RCBO based on the level of protection required.
- Bidirectional or Standard: If you have a solar panel or renewable energy system, opt for a bidirectional RCBO to handle two-way power flow.
11. The Future of Type A RCBOs and Renewable Energy
As the world shifts towards renewable energy, Type A RCBOs will continue to play a critical role in ensuring electrical safety. The growing adoption of solar panels, battery storage systems, and electric vehicles means more homes will require RCBOs that can handle bidirectional current flow and pulsating DC currents.
In the future, we may see even more advanced RCBOs that integrate with smart home systems, allowing homeowners to monitor and control their electrical systems remotely. This will not only improve convenience but also enhance safety by enabling quicker responses to potential faults.
12. Common Issues and Troubleshooting RCBOs
Even with the best equipment, things can go wrong. Here are some common issues you may encounter with Type A RCBOs and how to troubleshoot them:
Nuisance Tripping
If your RCBO trips frequently without an obvious fault, it could be due to a sensitive appliance or overloaded circuit. Try unplugging devices one by one to identify the cause.
RCBO Won’t Reset
If the RCBO refuses to reset after tripping, it’s important to identify the fault before attempting to reset it. Call a qualified electrician to troubleshoot the issue.
Regular Testing
Make sure to test the RCBO regularly to ensure it’s working properly. Most manufacturers recommend pressing the test button every six months.
13. Conclusion
Type A RCBOs are an essential component of any modern electrical system, offering protection from both overcurrent and earth faults, and they are particularly well-suited for homes with modern appliances and renewable energy systems. Whether you’re looking to upgrade your home’s electrical safety or ensure compliance with the latest regulations, investing in a Type A RCBO is a smart move.
By choosing the right RCBO for your needs—whether it’s a single pole, double pole, or bidirectional RCBO—you can ensure your home’s wiring is protected from a wide range of potential hazards. And with the future of energy moving towards renewables and smart home integration, Type A RCBOs will continue to play a crucial role in safeguarding our electrical systems.
- Compact Horizontal TP&N Distribution Boards – With 100A Main Switch & Type 2 SPD Options
- 🧱 Large PVC Cable Trunking by Dietzel Univolt – Key Sizes + Accessories
- How to Choose an LED Driver – Constant Voltage vs Constant Current Explained
- Most Popular FuseBox Consumer Units
- 🔌 Commando Sockets – The Ultimate Guide to Industrial Plugs and Sockets (IEC 60309)