A Comprehensive Guide to Buying a Consumer Unit: What You Need to Know from Start to Finish
Purchasing a consumer unit, often referred to as a fuse board, is one of the most important decisions a homeowner can make regarding the safety and efficiency of their electrical system. Whether you’re upgrading an old system, expanding your current one, or just looking to future-proof your home, choosing the right consumer unit is crucial. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know before making this important investment, from understanding the role of your existing unit to the installation of your new one by a fully qualified electrician.
What is a Consumer Unit?
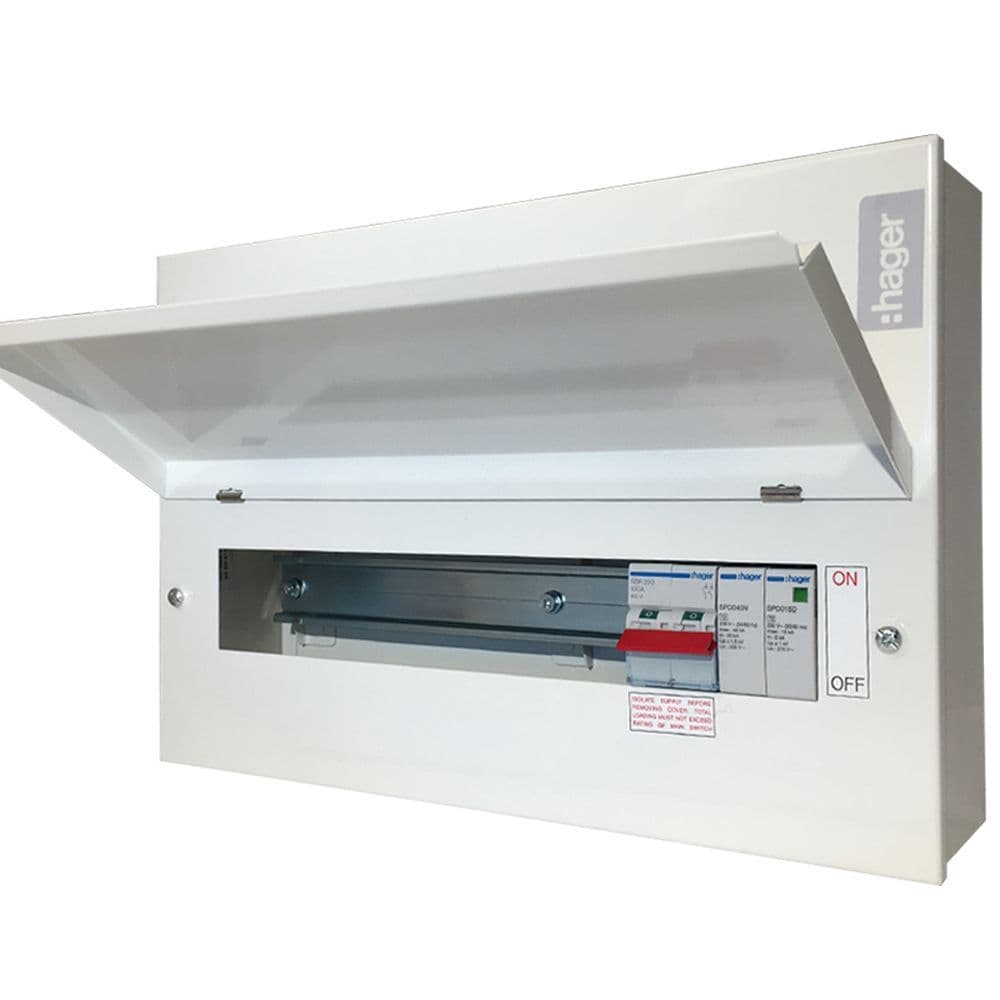
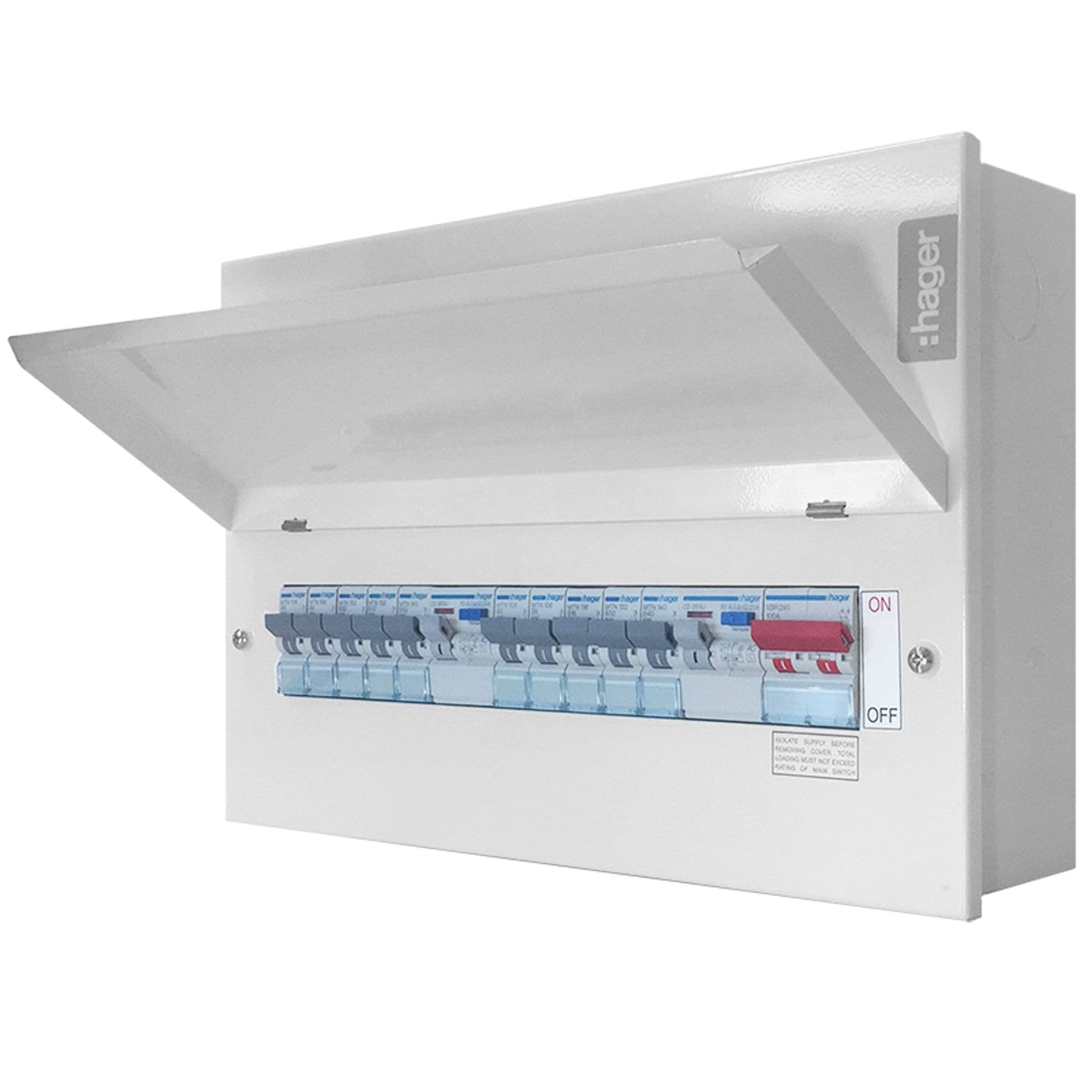
A consumer unit is the heart of your home’s electrical system. It distributes electricity throughout your house, ensuring that different circuits are protected by individual circuit breakers. The most basic function of a consumer unit is to prevent electrical overloads and short circuits by isolating faulty circuits to protect the rest of the system. Modern units come equipped with multiple protective devices that keep you and your home safe from electrical faults.
Understanding Your Existing Consumer Unit
Before purchasing a new consumer unit, it’s essential to assess your current setup. Many older homes have outdated fuse boards, which use fuses instead of circuit breakers. These systems can be inefficient and may not meet modern safety standards, increasing the risk of electrical fires or shocks.
Look at the condition of your existing unit. If it’s over 20 years old or shows signs of wear, such as melted fuses, corrosion, or an overloaded appearance, it’s time for an upgrade. An electrician can help identify whether your consumer unit complies with current regulations and whether you need to upgrade to meet legal and safety requirements.
What to Consider in Your New Consumer Unit
When buying a new consumer unit, there are several key considerations. Your choice will depend on the size of your home, the number of circuits you need, and the specific safety features you require. Here’s a breakdown of the essential factors:
1. Number of Circuits
Ensure your consumer unit has enough circuits to cover your home’s needs. Each major area (kitchen, living room, bathroom) will likely need its own circuit, as will high-demand appliances like electric showers, ovens, or washing machines.
2. Room for Expansion
If you’re considering future-proofing, look for a consumer unit with spare capacity. This will allow you to add more circuits later, whether you’re installing new appliances, converting a loft, or adding an extension.
3. RCBOs, MCBs, SPDs, and AFDDs
Modern consumer units come with an array of protective devices. Understanding how each works will help you make an informed decision.
MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers)
MCBs protect individual circuits from overloads and short circuits. When too much current flows through a circuit, the MCB automatically trips, preventing damage or fire. Each MCB is dedicated to a specific circuit.
RCBOs (Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent Protection)
RCBOs combine the functions of MCBs and RCDs. They not only protect against overcurrent but also provide protection against earth faults. RCBOs are ideal for protecting individual circuits, ensuring that if one trips, the rest of the circuits stay unaffected.
SPDs (Surge Protection Devices)
Surge Protection Devices safeguard your home against voltage spikes, which can be caused by lightning strikes, power outages, or faulty appliances. SPDs protect sensitive electronic equipment, such as computers and TVs, from damage.
AFDDs (Arc Fault Detection Devices)
Arc Fault Detection Devices detect electrical arcs that could lead to fires. Arcing can happen due to damaged wires, loose connections, or deteriorating cables. AFDDs are becoming more common in new consumer units and are highly recommended for enhanced fire protection.

4. Nuisance Tripping
Nuisance tripping occurs when circuit breakers trip unnecessarily. This can happen if multiple devices on the same circuit draw a lot of power at once, even when there’s no electrical fault. To minimize this, choose a consumer unit with RCBOs, which protect individual circuits more precisely, reducing the chances of all circuits being shut off when one issue occurs.
Future-Proofing Your Consumer Unit
Your consumer unit should serve your household for many years, so it’s important to choose one that is future-proofed. Here are some key factors to consider for longevity:
- Spare Capacity: As mentioned earlier, ensure the unit has extra slots for additional circuits.
- Modern Protection Devices: Opt for units with RCBOs and AFDDs for optimal protection.
- Smart Home Integration: Some modern consumer units offer smart features, allowing you to monitor power usage and control circuits remotely.
Electrical Regulations for Consumer Units
In the UK, all consumer units must comply with the latest electrical safety regulations. The current standard is the 18th Edition of the Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2018), which includes guidance on installing AFDDs, SPDs, and the proper use of RCBOs. If you’re unsure whether your consumer unit meets these standards, a qualified electrician can assess your system and recommend updates.
Key Requirements:
- Metal Enclosure: Since 2015, all new cu’s must be housed in a metal enclosure to reduce the risk of fire.
- RCD Protection: Residual Current Devices (RCDs) are required to protect against electric shocks.
- AFDDs for Certain Circuits: The 18th Edition recommends AFDDs for circuits in high-risk locations, like bedrooms or living rooms.
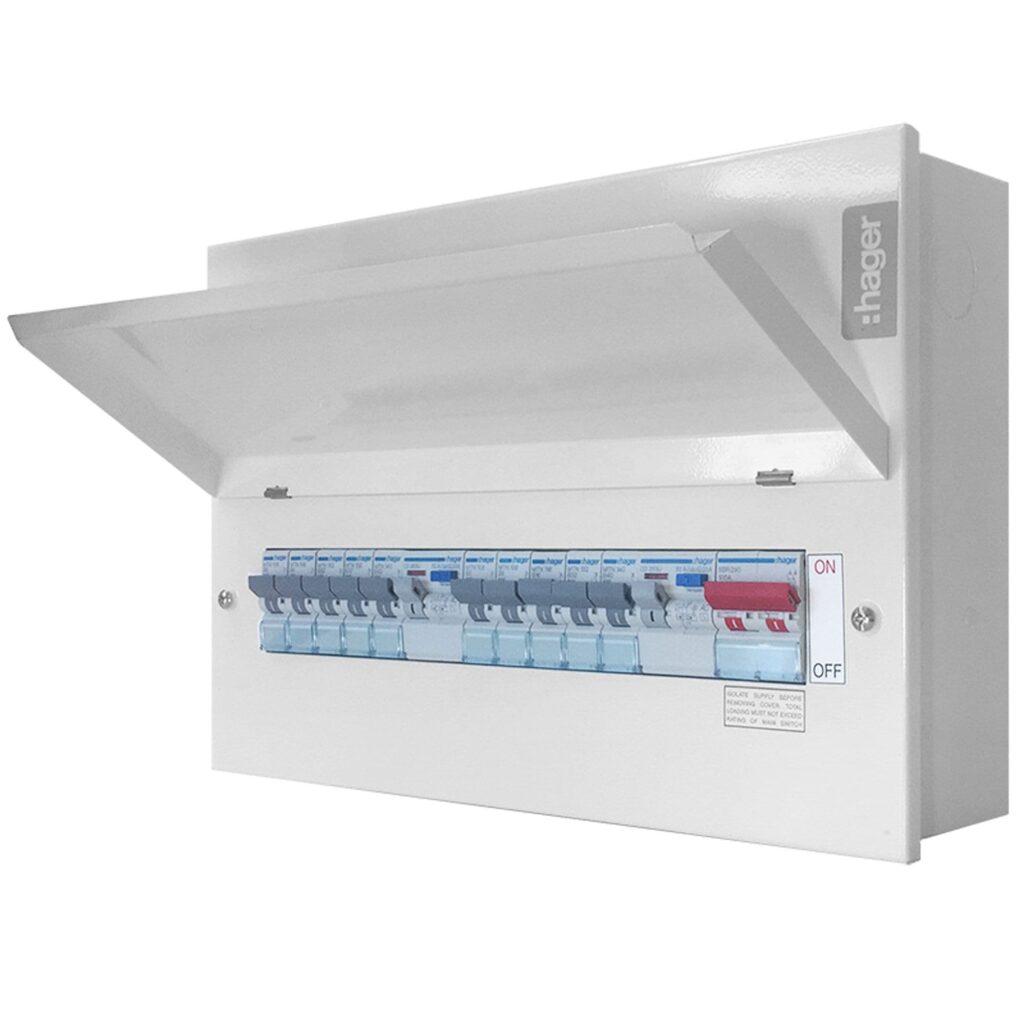
Types of Consumer Units
There are various types of consumer units available, and your choice depends on your household’s needs:
- Main Switch: This basic model contains a main switch and individual MCBs for circuit protection.
- Dual RCD: Equipped with two RCDs, this unit provides better protection, ensuring that if one circuit trips, others are still operational.
- RCBO Consumer Unit: This option allows for an individual RCBO for each circuit, providing enhanced protection and reducing nuisance tripping.
- High Integrity : Combines the advantages of dual RCD and RCBO units, offering flexibility, protection, and spare capacity for future expansion.
Brands to Consider: FuseBox, Hager, Live & WCED
FuseBox
FuseBox is known for its high-quality and affordable consumer units, making them popular among electricians and homeowners. They offer a wide range of units that meet the latest safety standards, including models with AFDDs and SPDs. FuseBox is perceived as a reliable and cost-effective option for those looking to upgrade their home’s electrical system.

Hager
Hager is a global leader in electrical distribution systems, with a strong reputation for innovative and user-friendly products. Their consumer units are widely respected for their durability and advanced safety features. Hager units are often chosen for both residential and commercial properties due to their robust design and easy installation process.

Live
Live is a trusted brand known for its attention to safety and quality. Their consumer units are versatile and include options for small and large installations. Live units are often praised for their flexibility, making them suitable for a range of home configurations.
WCED
WCED has a long history of manufacturing high-quality consumer units. Their products are known for being well-engineered, and they offer a wide range of options from basic models to highly advanced units with cutting-edge safety features. Wylex is a well-established name, synonymous with durability and safety in the electrical industry.
The Buying Process
When buying a consumer unit, it’s essential to follow a clear process to ensure you get the right system for your needs. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
1. Assess Your Current Electrical System
Have a qualified electrician assess your current consumer unit and wiring. They can advise you on whether your system meets modern standards and recommend any upgrades.
2. Determine Your Requirements
Consider the number of circuits you need, any future expansion plans, and whether you want the additional protection offered by RCBOs, SPDs, and AFDDs.
3. Choose the Right Consumer Unit
Select a consumer unit from a trusted brand that meets your specific needs. Ensure it complies with the latest regulations and offers future-proofing capabilities.
4. Hire a Qualified Electrician
A consumer unit must be installed by a fully qualified electrician. They will ensure the system is installed safely, configured correctly, and complies with local building and electrical codes.
5. Register the Installation
Once installed, your electrician will need to register the installation with your local building authority. This ensures that the work meets all legal and safety standards.
Conclusion
Upgrading or purchasing a new consumer unit is a significant investment in your home’s electrical safety. By understanding your existing setup, knowing what features you need, and choosing a reputable brand, you can make an informed decision that will protect your home for years to come. Always consult with a fully qualified electrician to ensure your consumer unit is properly installed and compliant with the latest regulations.
See our full range of consumer units here!