Estimated reading time: 11 minutes
Table of contents
- What is a Consumer Unit?
- What is Inside a Consumer Unit?
- Bidirectional RCBOs: A Modern Solution for Enhanced Safety
- Nuisance Tripping: Causes and Solutions
- Common Consumer Unit Accessories
- What Type of Consumer Unit Do I Need?
- How Do the Main Types of Consumer Units Vary?
- Can I Replace My Consumer Unit Myself?
- Conclusion

The consumer unit stands as the most vital electrical component inside any home, controlling and distributing power safely and efficiently. Beyond its operational roles, it serves as a critical safeguard against potential electric shock or fatal accidents. This comprehensive guide will cover the essentials of consumer units, including their components, types, and the considerations for their installation and maintenance.
What is a Consumer Unit?
A consumer unit, often referred to as a fuse box or distribution board, is an essential device in any electrical system. It is designed to protect against electric shock and manage the distribution of electrical power throughout a home. In the event of an electrical fault, the consumer unit is the first line of defense, ensuring that circuits are isolated to prevent accidents and damage. Knowing the location of your consumer unit is vital for quickly isolating power during an emergency.
What is Inside a Consumer Unit?
The components within a consumer unit each play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and functionality of the electrical system. Here’s a detailed look at each part:
Enclosure
The enclosure is the protective casing that houses all the components of the consumer unit. Since the introduction of the 18th edition regulations, all new installations must use a steel enclosure. This metal casing provides enhanced fire resistance compared to older plastic units.
Earth Bar
The earth bar is a common connection point for all the circuits’ earth cables. It ensures that all circuit protective conductors, including those for earth bonding, are properly connected. This component is vital for preventing electric shock by providing a path to ground in the event of a fault.
Neutral Bars
Neutral bars serve as common connection points for the neutral cables from the earth leakage protection devices, such as RCBOs. They play a key role in maintaining the balance of the electrical system and ensuring safe operation.
Din Rail
The din rail is a metal bar inside the consumer unit where all circuit protection devices are mounted. It faces outwards and is designed to hold components like MCBs and RCBOs securely. The din rail does not carry any electrical current but provides structural support for the components.
Busbar
The busbar is a long strip of copper with ‘teeth’ that lock circuit breakers and the main switch securely. It distributes electrical power from the main switch to the individual circuit breakers, ensuring that each circuit receives the appropriate voltage.
Main Switch
The main switch controls the electrical supply to the entire home. It allows for the isolation of all circuits by simply turning it on or off. This switch is essential for emergency situations, providing a quick and easy way to cut off the electrical supply.
MCB (Mini Circuit Breaker)
MCBs protect individual circuits from overload and short circuits. They come in various amperages, typically ranging from 6A to 50A in domestic installations. An MCB will trip and cut off power to a circuit if it detects an overload, preventing potential damage and fire hazards.
RCD (Residual Current Device)
RCDs protect against electric shock by monitoring the balance between the live and neutral wires. If there is a discrepancy, indicating a leakage of current, the RCD will trip and cut off power. This device is crucial for preventing electrical accidents.
RCBO (Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent)
RCBOs combine the functions of an MCB and an RCD, providing protection against both overloads and earth leakage. They are increasingly popular due to their enhanced safety features and are often recommended for new installations despite their higher initial cost.
Blanks
Blanks are pieces of plastic that clip onto the din rail to cover unused slots. They allow for future expansion of the consumer unit without requiring reconfiguration. This flexibility is useful for adding new circuits, such as outdoor lighting or additional outlets.
SPD (Surge Protection Device)
SPDs protect the electrical system from power surges, which can be caused by lightning strikes or other external factors. These devices are now a requirement under the 18th edition regulations and are installed between the outside feed and the main switch.
AFDD (Arc Fault Detection Device)
AFDDs detect arc faults, which occur when electrical currents jump the gap between two conductive materials. Arcs can generate high temperatures and are a leading cause of domestic fires. AFDDs provide an additional layer of protection by detecting and mitigating these faults.

Bidirectional RCBOs: A Modern Solution for Enhanced Safety
Bidirectional RCBOs represent a significant advancement in electrical safety technology. Traditional RCBOs operate in a unidirectional manner, monitoring current flow in one direction. However, with the increasing complexity of modern electrical systems, especially those involving renewable energy sources like solar panels, the need for bidirectional RCBOs has become more apparent.
What are Bidirectional RCBOs?
Bidirectional RCBOs can detect faults in both directions of current flow. This is particularly important in systems where power can be fed back into the grid, such as homes with solar panels. These RCBOs provide comprehensive protection by ensuring that any irregularities in the current, whether from the grid or from the home, are detected and isolated.
Why Are They Becoming More Popular?
As the adoption of renewable energy sources grows, so does the complexity of home electrical systems. Bidirectional RCBOs offer a robust solution for managing these complexities. They provide enhanced safety by protecting against reverse current flow, which can occur in systems with energy storage or generation capabilities. This added layer of protection helps prevent potential hazards associated with bidirectional power flow, making these RCBOs increasingly popular in modern installations.

Nuisance Tripping: Causes and Solutions
Nuisance tripping is a common issue that many homeowners face. It occurs when an RCD or RCBO trips without a clear cause, disrupting power and causing inconvenience. Understanding the causes and solutions for nuisance tripping can help maintain a stable and reliable electrical system.
Common Causes of Nuisance Tripping
- Overloaded Circuits: One of the most common causes of nuisance tripping is circuit overload. When too many devices are plugged into a single circuit, it can exceed the circuit’s capacity, causing the RCD or RCBO to trip.
- Faulty Appliances: Electrical appliances that have faults or are damaged can cause an imbalance in the current, leading to tripping. Regular maintenance and checks of household appliances can help identify and fix these issues.
- Moisture and Humidity: In areas with high humidity or where water ingress is possible, such as kitchens, bathrooms, or outdoor installations, moisture can cause nuisance tripping. Ensuring proper sealing and protection of electrical components in these areas is essential.
- Wiring Issues: Loose connections, damaged wires, or poor installation practices can create intermittent faults that lead to tripping. Regular inspection and maintenance by a qualified electrician can help identify and rectify these issues.
- External Factors: Power surges from the main supply, lightning strikes, or other external factors can cause sudden tripping. Installing SPDs can help mitigate the impact of these surges.
Solutions to Prevent Nuisance Tripping
- Circuit Separation: Distributing the load more evenly across multiple circuits can prevent overloads. This might involve adding new circuits or redistributing existing loads.
- Regular Maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance of the electrical system, including checking for loose connections and damaged wires, can prevent faults that cause tripping.
- Upgrade to RCBOs: Upgrading to RCBOs can help isolate faults to specific circuits, reducing the impact of a single fault on the entire electrical system.
- Environmental Controls: Installing dehumidifiers or ensuring proper ventilation in humid areas can reduce the risk of moisture-related tripping.
- Professional Inspection: Having a qualified electrician inspect your electrical system periodically can help identify potential issues before they become major problems.
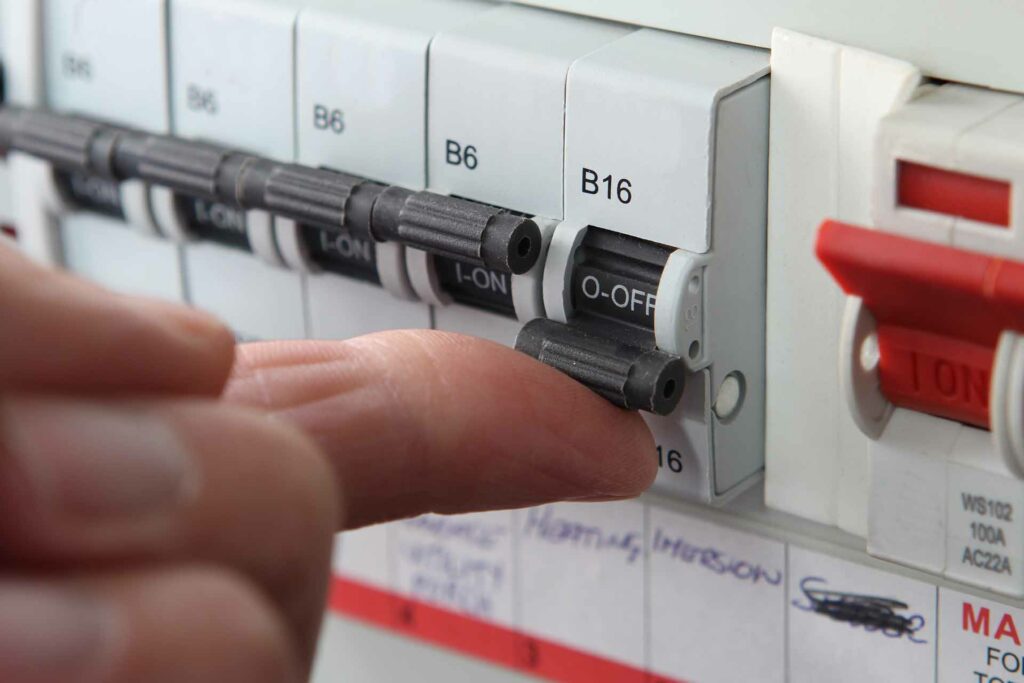

Common Consumer Unit Accessories
A well-functioning consumer unit often requires various accessories to ensure optimal performance and safety. Here’s an overview of some common accessories:
Flexi Tails
Flexi tails are flexible cables used to connect the consumer unit to the main incoming supply. They are designed to be easily maneuvered, making installation simpler and more efficient.
Grommets
Grommets are used to protect cables as they pass through the metal edges of the consumer unit. They prevent damage to the insulation, which can lead to shorts or electrical faults.
Cable Glands
Cable glands secure and protect cables entering the consumer unit. They ensure that the cables remain firmly in place and provide a seal against dust and moisture.
Blanks
Blanks cover unused slots on the din rail, preventing accidental contact with live parts and allowing for future expansion of the consumer unit.
Rear Entry Grommets
These grommets are used when cables enter the consumer unit from the rear. They provide a smooth entry point, protecting cables from abrasion and damage.
Grommet Strip
A grommet strip is a flexible piece of material that lines the edges of holes where cables pass through. It offers additional protection against wear and tear.
Henley Blocks
Henley blocks are connectors used to join multiple cables together. They are often used when splitting the main incoming supply to feed more than one consumer unit.
Earth Blocks
Earth blocks provide a common point for connecting earth conductors within the consumer unit. They ensure all earth connections are secure and reliable.
Bell Transformers
Bell transformers step down the voltage from the consumer unit to a suitable level for doorbells and other low-voltage devices.
Din Rail Timers
Din rail timers are mounted inside the consumer unit and used to control lighting and other circuits based on a set schedule. They help improve energy efficiency and convenience.
Single Phase Energy Meters
These meters measure the energy consumption of a single-phase electrical installation. They are useful for monitoring and managing energy use.

What Type of Consumer Unit Do I Need?
Choosing the right type of consumer unit depends on several factors, including the size of your home, the complexity of your electrical system, and your specific needs. Here are the main types of consumer units:
Main Switch Consumer Unit
This type is the most common and versatile, complying fully with the 18th edition regulations. It uses RCBOs for individual circuit protection, making it a preferred choice for modern installations. These units offer the flexibility to add surge protection devices (SPDs) and other components as needed.
Dual RCD Consumer Unit
Dual RCD units feature a main switch and two RCDs. While cost-effective, they require careful circuit design to avoid issues such as losing power to all lighting circuits simultaneously during a fault. They provide a good balance between safety and cost for many homes.
RCD Incomer Consumer Unit
Commonly used in outbuildings like garages and sheds, these units do not have a main switch and rely on a single RCD for isolation. They are suitable for simpler installations with fewer circuits.
High Integrity Consumer Unit
High integrity units come with three neutral bars, allowing for more flexible circuit management. They enable a mix of RCBOs and MCBs, providing enhanced protection and design flexibility for critical circuits.
How Do the Main Types of Consumer Units Vary?
Understanding the differences between consumer unit types helps in making an informed choice. Here’s a closer look:
Amendment 3 Consumer Unit
These are the most common units, typically made of metal for enhanced fire resistance. They vary in size based on the number of circuits, such as 10-way or 14-way units.
Duplex Consumer Unit
A duplex unit features two consumer units stacked together. They are ideal for larger installations requiring extensive circuit separation and management, particularly in compliance with modern regulations.
Flush Consumer Unit
Designed for modern aesthetics, flush consumer units integrate seamlessly into walls, making them less obtrusive. They offer the same functionality as standard units but with a more streamlined appearance.
Garage Consumer Unit
These compact units, typically with up to four ways, are used in outbuildings. They provide necessary circuit protection for lighting and tools, tailored to smaller, simpler electrical systems.
EV Consumer Unit
With the rise of electric vehicles, EV consumer units have become increasingly important. These units come equipped with a 100A main switch and Type 2 surge protection, designed to support EV charging installations.
Can I Replace My Consumer Unit Myself?
Replacing a consumer unit is a complex task that should only be performed by a fully qualified electrician. Attempting to replace your own consumer unit is not only illegal but also highly dangerous. Incorrect installation can result in serious injury, electric shock, or fire. A certified professional will ensure that the installation complies with all relevant regulations and standards, providing peace of mind and enhanced safety for your home.
Conclusion
Consumer units are indispensable for ensuring the safety and efficiency of a home’s electrical system. Understanding their components, the different types available, and the importance of regular maintenance can help homeowners make informed decisions about their electrical infrastructure. Incorporating modern advancements like bidirectional RCBOs and using appropriate accessories can further enhance the safety and reliability of your electrical system. By staying informed and vigilant, you can ensure that your consumer unit provides reliable protection and power distribution for years to come.
- Compact Horizontal TP&N Distribution Boards – With 100A Main Switch & Type 2 SPD Options
- 🧱 Large PVC Cable Trunking by Dietzel Univolt – Key Sizes + Accessories
- How to Choose an LED Driver – Constant Voltage vs Constant Current Explained
- Most Popular FuseBox Consumer Units
- 🔌 Commando Sockets – The Ultimate Guide to Industrial Plugs and Sockets (IEC 60309)