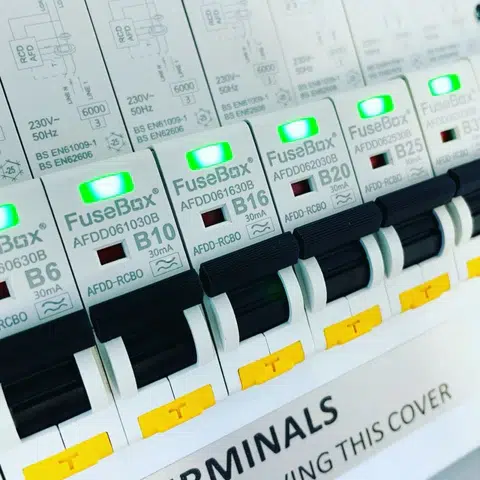
Arc Fault Detection Devices (AFDDs) have become crucial components in modern electrical safety systems. Their ability to detect and mitigate electrical arcing faults helps prevent potential fires, making them an essential part of residential and commercial installations. This comprehensive guide will explore the history and advancements of AFDD technology, the 18th edition wiring regulations, and the leading brands in the market, including Fusebox, Hager, and Live. We’ll also delve into the technical details of their AFDD offerings and provide answers to frequently asked questions.
The History and Evolution of AFDDs
AFDDs were developed in response to the need for enhanced electrical safety. Traditional circuit breakers and RCDs (Residual Current Devices) could protect against overloads and earth faults, but they could not detect electrical arcs. Arcing occurs when electrical connections become loose or damaged, creating high-temperature sparks that can ignite surrounding materials.
The concept of AFDDs originated in the late 20th century, with the first devices introduced in the early 2000s. Early AFDDs were relatively basic and often faced reliability issues. However, technological advancements have significantly improved their performance and reliability.
Modern AFDDs use sophisticated electronic sensors and algorithms to detect the unique signature of electrical arcs. They can distinguish between harmless arcs, like those from a switch, and dangerous arcs that can cause fires. These advancements have made AFDDs an invaluable tool in preventing electrical fires and enhancing overall safety.
Advancements in AFDD Technology
Over the years, AFDD technology has seen several significant advancements. Early devices were often prone to nuisance tripping, where the device would shut off power in response to benign electrical activity. Modern AFDDs have improved discrimination capabilities, reducing false alarms while maintaining high sensitivity to hazardous arcs.
Another important advancement is the integration of AFDDs with other protective devices. Many modern AFDDs are combined with RCBOs (Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent protection), providing comprehensive protection against overloads, short circuits, earth faults, and arcing faults in a single device.
Additionally, today’s AFDDs come with features like self-testing and real-time monitoring, ensuring that they are always ready to protect the electrical system. These innovations have made AFDDs more reliable, user-friendly, and effective in preventing electrical fires.

The 18th Edition Wiring Regulations
The 18th edition wiring regulations, introduced in 2018, set new standards for electrical installations in the UK. These regulations emphasize the importance of using AFDDs in certain situations to enhance safety.
According to the regulations, AFDDs are recommended for circuits that supply socket outlets in:
- Premises with sleeping accommodation (e.g., homes, hotels, and hospitals).
- Locations with a higher risk of fire due to the nature of processed or stored materials (e.g., woodworking shops).
- Public buildings (e.g., schools, theaters, and museums).
- Locations with end-user vulnerability (e.g., care homes).
These recommendations aim to reduce the risk of electrical fires, especially in environments where the consequences of a fire could be severe. While not yet mandatory in all installations, the use of AFDDs is strongly encouraged to enhance safety.
Leading Brands and Their AFDD Offerings
1. Fusebox: Fusebox is known for its high-quality consumer units and protective devices, including AFDDs. Established in Kilmarnock, Scotland, in 2017, Fusebox quickly gained a reputation for its reliable and user-friendly products. Key features of Fusebox AFDDs include:
- Integration with RCBOs for combined protection.
- Advanced arc detection algorithms to minimize false trips.
- Real-time status indicators and self-testing capabilities.
Fusebox’s commitment to quality and innovation makes their AFDDs a trusted choice for both residential and commercial installations. Their products are designed to be installer-friendly, ensuring ease of use and reliability.

2. Hager: Hager is a well-established name in the electrical industry, offering a wide range of protective devices, including AFDDs. Hager AFDDs are known for their advanced technology and robust performance. Key features include:
- High discrimination capabilities to reduce nuisance tripping.
- Combination with RCBOs for comprehensive protection.
- Modular design for easy installation and maintenance.
Hager’s AFDDs are designed to meet the highest safety standards, ensuring reliable protection against electrical arcs. The company’s focus on innovation and customer satisfaction makes them a trusted choice for electricians and homeowners alike.

3. Live: Live Electric offers a range of AFDDs known for their efficiency and reliability. Their products are designed to provide comprehensive protection for electrical systems, ensuring long-term safety and performance. Highlights include:
- Multi-stage protection to address various types of electrical faults.
- Compact and durable construction for easy integration.
- Real-time monitoring and status indicators.
Live Electric’s AFDDs are designed to offer maximum protection with minimal maintenance, making them an ideal choice for both residential and commercial installations. The company’s focus on durability ensures that their products can withstand the rigors of everyday use, providing reliable protection for years to come.
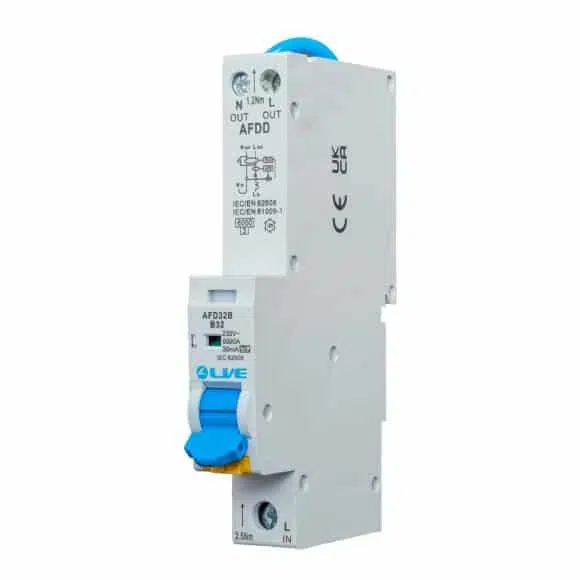

Technical Details of AFDDs
AFDDs are designed to detect two main types of electrical arcs: series and parallel arcs.
- Series Arcs: Occur when there is a break in the conductor, causing an intermittent connection.
- Parallel Arcs: Occur between two conductors, often caused by insulation failure.
AFDDs monitor the electrical circuit for the specific signature of these arcs, which involves high-frequency noise and specific voltage patterns. When an arc is detected, the AFDD interrupts the circuit, preventing potential fires.
Modern AFDDs combine arc detection with other protective functions, such as overcurrent and earth fault protection. This combination ensures comprehensive safety for electrical systems, protecting against a wide range of faults.
Conclusion
Arc Fault Detection Devices (AFDDs) play a critical role in modern electrical safety, providing protection against potentially hazardous electrical arcs. The advancements in AFDD technology, combined with the recommendations of the 18th edition wiring regulations, emphasize the importance of these devices in preventing electrical fires. Leading brands like Fusebox, Hager, and Live offer high-quality AFDDs with advanced features, ensuring reliable and comprehensive protection. Understanding the importance of AFDDs and choosing the right one for your specific needs can enhance safety and protect your property from electrical fires.
AFDD FAQ
AFDDs are recommended but not mandatory in all installations according to the 18th edition wiring regulations.
An AFDD detects dangerous electrical arcs and interrupts the circuit to prevent potential fires.
An RCBO provides protection against overloads, short circuits, and earth faults, while an AFDD specifically detects and mitigates electrical arcs.
An AFDD does not detect overloads, short circuits, or earth faults. It focuses on detecting electrical arcs.
AFDDs are recommended for circuits supplying socket outlets in specific high-risk areas but not necessarily on every circuit.
AFDDs should be fitted in circuits with high fire risk, such as sleeping accommodations, public buildings, and locations with end-user vulnerability.
Arc fault protection is not required in circuits without socket outlets or in low-risk areas not specified by regulations.
Many modern AFDDs are combined with RCBOs, providing both arc fault detection and RCD protection.
Yes, AFDDs can be used on ring circuits to detect and mitigate electrical arcs.
AFDDs can be tested using specialized testing devices that simulate arc faults, ensuring the AFDD operates correctly.
Circuits supplying socket outlets in high-risk areas, such as bedrooms, living rooms, and kitchens, should have arc-fault protection.
Install arc fault breakers in high-risk areas during new installations or when upgrading existing electrical systems.
Check your consumer unit for devices labelled as AFDD or consult an electrician to identify if you have arc fault protection.
AFDDs are designed to detect arcing by monitoring electrical circuits for high-frequency noise and specific voltage patterns.
Bathroom lights do not typically require arc fault protection unless specified by local regulations or specific risk assessments.
Arc fault breakers trip easily to provide maximum protection against potential fire hazards caused by electrical arcs.
Garage circuits should have arc fault protection if they supply socket outlets, especially if the garage contains flammable materials.
Avoid using arc fault breakers in circuits where they could interfere with critical safety functions or where not recommended by manufacturers.
Bedroom lights do not typically require arc fault breakers unless they are part of a circuit supplying socket outlets.
Smoke detectors do not require arc fault breakers but should be on a dedicated circuit with appropriate protection.
Yes, kitchens often have a high concentration of electrical devices, making arc fault protection essential for safety.
Arc fault breakers are not mandatory in older homes but are recommended when upgrading electrical systems for enhanced safety.
AFDDs are mandatory in certain high-risk areas as specified by the 18th edition wiring regulations, such as sleeping accommodations and public buildings.
AFDDs offer enhanced safety by detecting and mitigating electrical arcs, reducing the risk of electrical fires.
AFDDs detect series arcs, caused by breaks in conductors, and parallel arcs, caused by insulation failure between conductors.
The British Standard for AFDDs is BS EN 62606.
Check for labelling indicating AFDD or consult an electrician to identify if your breaker includes arc fault protection.
Yes, Fusebox manufactures AFDDs with advanced features and reliable performance.
Fusebox AFDDs are known for their quality, reliability, and user-friendly design, making them a popular choice among electricians.
Yes, Hager produces high-quality AFDDs with advanced technology and robust performance.
Hager AFDDs are well-regarded for their reliability, advanced features, and high discrimination capabilities, reducing nuisance tripping while ensuring safety.
- Compact Horizontal TP&N Distribution Boards – With 100A Main Switch & Type 2 SPD Options
- 🧱 Large PVC Cable Trunking by Dietzel Univolt – Key Sizes + Accessories
- How to Choose an LED Driver – Constant Voltage vs Constant Current Explained
- Most Popular FuseBox Consumer Units
- 🔌 Commando Sockets – The Ultimate Guide to Industrial Plugs and Sockets (IEC 60309)