What Are AFDDs and Why Are They Used?
Arc Fault Detection Devices (AFDDs) are advanced safety devices designed to protect electrical installations from arc faults. Arc faults occur when there is a breakdown in the electrical insulation, leading to an unintended flow of electricity through an arc. These faults can generate high temperatures and potentially cause fires. AFDDs are specifically engineered to detect these dangerous conditions and disconnect the power supply to prevent accidents.
The primary purpose of AFDDs is to enhance electrical safety by identifying and mitigating arc faults before they can escalate into hazardous situations. Traditional circuit protection devices, such as Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) and Residual Current Devices (RCDs), are effective against overcurrents and earth faults but may not detect the subtle signs of arc faults. AFDDs fill this critical gap by providing an additional layer of protection.
Technical Details About The Fusebox AFDD Range
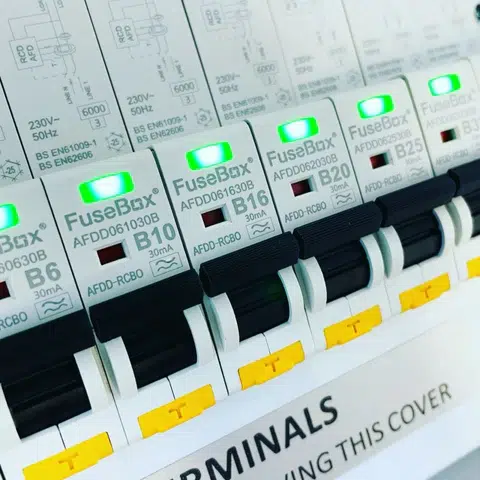
Fusebox, a leading brand in the electrical industry, offers a range of high-quality AFDDs designed to meet the stringent requirements of modern electrical installations. Fusebox AFDDs incorporate state-of-the-art technology to ensure reliable and efficient arc fault detection.
Key Features of Fusebox AFDDs
- Advanced Detection Technology: Fusebox AFDDs use sophisticated algorithms to identify both series and parallel arc faults. This ensures comprehensive protection across various types of electrical faults.
- Integrated Protection: Fusebox AFDDs often combine arc fault detection with overcurrent and earth fault protection. This integration means that a single device can perform the functions of an AFDD, an MCB, and an RCD, offering a compact and efficient solution for electrical safety.
- User-Friendly Design: Fusebox AFDDs are designed with ease of installation and operation in mind. They feature clear status indicators and straightforward test mechanisms, making them accessible for both professional electricians and end-users.
- Compliance with Standards: Fusebox AFDDs comply with the latest electrical safety standards, including the 18th Edition Wiring Regulations. This ensures that installations using Fusebox AFDDs meet current safety and performance criteria.
Who Is Fusebox?
Fusebox is a renowned brand in the electrical industry, known for producing high-quality consumer units and protective devices. With a commitment to innovation and safety, Fusebox has established itself as a trusted name among electricians and homeowners alike.
Fusebox products are designed to provide reliable performance and ease of use. Their range includes consumer units, RCDs, RCBOs, and AFDDs, all engineered to the highest standards. Fusebox’s dedication to quality and customer satisfaction makes them a preferred choice for electrical safety solutions.
Understanding the 18th Edition Wiring Regulations
The 18th Edition Wiring Regulations, introduced in July 2018, are the latest set of standards governing electrical installations in the UK. These regulations, also known as BS 7671:2018, aim to improve safety, efficiency, and reliability in electrical systems. Key aspects of the 18th Edition Wiring Regulations include:
- Enhanced Protection Measures: The regulations emphasize the importance of RCD protection for all final circuits in residential installations. This helps prevent electric shock and other electrical hazards.
- Surge Protection: The 18th Edition mandates the use of Surge Protection Devices (SPDs) in certain installations to protect against transient overvoltages caused by lightning strikes or switching operations.
- Arc Fault Detection: One of the notable additions in the 18th Edition is the recommendation for the use of AFDDs in specific high-risk locations. While not yet mandatory, this recommendation highlights the growing recognition of AFDDs’ role in preventing electrical fires.
- Energy Efficiency: The regulations include provisions for improving the energy efficiency of electrical installations, such as the use of energy-efficient lighting and controls.
Conclusion
Fusebox AFDDs represent a significant advancement in electrical safety technology. By detecting and mitigating arc faults, they provide essential protection that complements traditional circuit protection devices. Whether you are upgrading an existing installation or planning a new one, incorporating AFDDs from a reputable brand like Fusebox ensures enhanced safety and compliance with the latest standards. As the 18th Edition Wiring Regulations continue to shape the future of electrical installations, the use of AFDDs is poised to become an integral part of maintaining safe and reliable electrical systems.
In summary, AFDDs are a crucial component in modern electrical safety. Their ability to detect arc faults and prevent potential fires makes them indispensable in high-risk areas. By choosing Fusebox AFDDs, you are investing in state-of-the-art technology that prioritizes safety and reliability.
While AFDDs are highly recommended for high-risk areas such as bedrooms, living rooms, and other places with potential fire hazards, they are not mandatory for every circuit. However, incorporating AFDDs across more circuits can significantly enhance safety.
AFDDs should be installed in areas with higher risks of arc faults, such as circuits supplying sockets in living rooms, bedrooms, and other high-usage areas. It’s also advisable to follow the recommendations of the 18th Edition Wiring Regulations for specific installations.
No, AFDDs and RCBOs are different devices. An AFDD detects arc faults, while an RCBO (Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent protection) combines the functions of an RCD and an MCB, protecting against earth faults and overcurrents.
An AFDD is designed to detect arc faults but may not identify overcurrent conditions or earth faults unless it is integrated with these protections. Separate devices like MCBs and RCDs are required for comprehensive protection.
AFDDs typically have a built-in test button that simulates an arc fault. Pressing this button should cause the device to trip, indicating that it is functioning correctly. Regular testing is recommended to ensure ongoing protection.
Circuits not typically requiring arc fault protection include those dedicated to fixed equipment like ovens, boilers, and other heavy appliances, as these circuits are less likely to develop arc faults compared to general-purpose sockets.
Yes, AFDDs are effective at detecting and mitigating arc faults, significantly reducing the risk of electrical fires. Their advanced detection technology allows them to identify arc faults that other protective devices might miss.
While AFDDs are currently recommended in high-risk areas according to the 18th Edition Wiring Regulations, they are not mandatory across all circuits. However, as safety standards evolve, it is possible that their use may become more widespread and potentially mandatory in the future.
Arc fault breakers are not typically used on circuits dedicated to fixed appliances or in environments where arc fault detection might be impaired, such as certain industrial settings with significant electrical noise.
The flashing of an AFDD indicates a specific fault or condition. Refer to the manufacturer’s manual for exact diagnostics, but generally, multiple flashes may indicate a detected arc fault or a self-test error.
Yes, AFDDs can be used on ring circuits. They are designed to detect arc faults regardless of the circuit configuration, providing enhanced safety for various types of electrical installations.
An AFDD detects both series and parallel arc faults. Series arc faults occur in a single conductor, while parallel arc faults occur between two conductors.
AFDDs should be fitted in consumer units, protecting circuits supplying high-risk areas such as bedrooms, living rooms, and areas with high electrical usage.
Yes, Fusebox AFDDs are known for their reliability, advanced detection capabilities, and compliance with the latest safety standards, making them a good choice for enhancing electrical safety.
Arc-fault breakers should be installed in circuits supplying high-risk areas, such as living spaces with high electrical usage and sleeping areas, as recommended by the 18th Edition Wiring Regulations.
Yes, performing electrical work without the necessary qualifications and licensing is illegal in the UK. Only qualified electricians should carry out electrical installations and maintenance to ensure safety and compliance with regulations.
Yes, AFDDs can be retrofitted into existing consumer units, provided there is adequate space and the unit is compatible with the additional protection device.
AFDDs do not detect overcurrent conditions or earth faults on their own. These require additional protection devices such as MCBs and RCDs.
While not mandatory, it is advisable to provide arc-fault protection for outdoor plugs, especially if they are used frequently or for high-power devices.
Arc-fault protection is generally not required for circuits dedicated to fixed appliances like ovens and boilers, as these circuits are less likely to develop arc faults.
AFDDs significantly enhance safety by detecting arc faults that could lead to electrical fires, providing an additional layer of protection beyond traditional devices. They are especially useful in high-risk areas and can prevent potentially dangerous situations.
Circuits supplying sockets in living rooms, bedrooms, and other high-usage areas are recommended for arc-fault protection to prevent electrical fires and enhance safety.
While AFDDs often incorporate RCD functionality, the RCD test should be conducted separately using the test button specific to the RCD function to ensure it is working correctly.
RCBOs are not mandatory but are highly recommended for providing comprehensive protection against both earth faults and overcurrents. They are particularly useful for individual circuit protection.
Using arc-fault breakers is highly recommended in areas with high fire risk and significant electrical usage. They provide an additional layer of safety and can prevent electrical fires by detecting arc faults that other devices may miss.