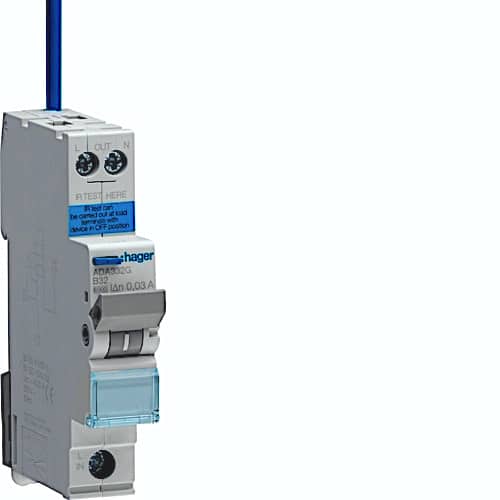
RCDs (Residual Current Devices) come in various forms and react differently based on the presence of DC components or different frequencies. Designers and installers must select the appropriate device for the specific application. Here are the main types of RCDs available, each with their respective symbols:
Type AC
This general-purpose RCD detects and responds to AC sinusoidal waves only.
Type A
Designed for equipment with electronic components, this RCD detects and responds to AC sinusoidal waves and pulsating DC components.
Type F
Ideal for equipment with frequency-controlled speed drives, this RCD detects and responds to AC sinusoidal waves, pulsating DC components, and high-frequency residual currents.
Type B
Used for electric vehicle chargers and PV supplies, this RCD detects and responds to AC sinusoidal waves, pulsating DC components, high-frequency residual currents, and smooth DC residual currents.
RCD Examples by Type of Equipment / Load
Type AC – General Purpose:
This type is suitable for resistive, capacitive, and inductive loads without electronic components, such as:
- Immersion heaters
- Ovens/Hobs with resistive heating elements
- Electric showers
- Tungsten and halogen lighting
Type A – Single Phase with Electronic Components:
This RCD is ideal for appliances with single-phase inverters and Class 1 IT and multimedia equipment, including:
- Power supplies for Class 2 equipment
- Washing machines (not frequency controlled, e.g., DC or universal motor)
- Lighting controls like dimmer switches and home/building electronic systems
- LED drivers
- Induction hobs
- Electric vehicle charging (smooth DC fault current < 6 mA)
Type F – Frequency Controlled Equipment / Appliances:
This type works best for appliances with frequency-controlled speed drives, such as:
- Some washing machines, dishwashers, and dryers with synchronous motors
- Some Class 1 power tools
- Air conditioning controllers using variable frequency speed drives
Type B – Three Phase Electronic Equipment:
This RCD is suitable for equipment with inverters for speed control and UPS systems, including:
- Electric vehicle charging (smooth DC fault current > 6 mA)
- Photovoltaic systems
- Power electronic converter systems (PECS)
- Industrial machines
- Cranes
Application Suitability
In addition to their primary uses:
- Type A is also suitable for Type AC applications.
- Type F is also suitable for Type AC and Type A applications.
- Type B is also suitable for Type AC, Type A, and Type F applications.
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate RCD type is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance in various electrical installations. Therefore, it is essential to understand the differences and applications of each RCD types